[2002.05.16] Nasal Osteotomy for Narrowing a Wide Nasal Bone
Date: May 16, 2002
Conference: 20th Meeting of the Korean Academy of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (Shilla Hotel, Jeju)
Title: Nasal Osteotomy for Narrowing a Wide Nasal Bone: Proposed Surgical Criteria for Korean Patients
Introduction
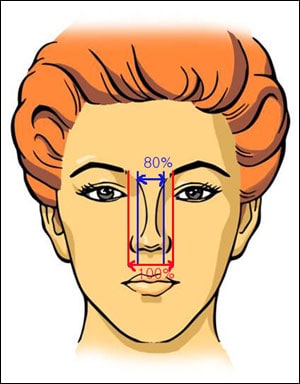
Asian nasal bones are often relatively short and wide. When performing rhinoplasty, attention is usually given to the nasal tip and dorsum; however, the lateral aspects of the nose can also be critical for achieving a balanced aesthetic result. Ideally, the nasal bone width should be about 80% of the interalar width. In this study, the authors propose more precise criteria for lateral osteotomy in Asian rhinoplasty, as well as a simplified method for performing it.
Methods and Materials
The authors studied 105 patients who underwent rhinoplasty for cosmetic purposes. They defined absolute indications for nasal osteotomy as cases where the nasal bone width exceeds the alar base width (≥ 100%), and relative indications for cases measuring between 80% and 100%.
Surgical Technique
Using a 2–3 mm osteotome, the authors most frequently performed percutaneous osteotomy of the lateral nasal wall. Prior to surgery, they marked the area to be osteotomized.
Results
- Follow-up Period: 4–15 months (average 6 months)
- Lateral Osteotomy Rate: Of the 105 patients, 58 (55%) required lateral osteotomy. Among those 58 patients, 33 (57%) underwent osteotomy to narrow the nasal width.
- Osteotomy Approaches:
- Low-to-High + Medial Oblique Osteotomy in 29 patients
- Low-to-Low + Paramedian + Transverse Osteotomy in 4 patients
- Osteotomy Technique:
- Percutaneous osteotomy was used in 31 patients.
- Endonasal osteotomy was used in 2 patients.
- Recovery: Patients who had percutaneous osteotomy experienced reduced swelling and bruising compared to those who had internal (endonasal) osteotomy.
Discussion
Percutaneous osteotomy minimizes injury to branches of the lateral nasal artery and reduces mucosal laceration. As a result, patients show less postoperative swelling and bruising, faster recovery, and more precise osteotomy results.
Conclusion
Due to ambiguous guidelines and the complexity of the technique, lateral osteotomy has often been overlooked in cases of wide nasal bones. However, 55% of the authors’ rhinoplasty patients met the absolute indication for osteotomy. Percutaneous osteotomy offered better surgical accuracy and quicker recovery compared to the traditional endonasal approach.