Male Facelift Surgery: What Makes it Different from Female Facelifts
The demand for facial rejuvenation procedures among male patients has increased significantly in the recent 5 years at VIP Clinic. Dr. Myung Ju Lee says that male facelift surgery have unique anatomical challenges that require specialized surgical planning and technique modifications. This blog post examines the specific considerations for male facelift procedures, focusing on anatomical differences, surgical techniques, and achieving natural-appearing results that maintain masculine facial characteristics.

Anatomical Differences in Male Patients
Skin and Soft Tissue Characteristics
Male facial skin demonstrates several distinct characteristics that directly impact surgical planning:
- Increased dermal thickness: Male skin is approximately 25% thicker than female skin, with thicker collagen fiber networks
- Stronger fascial attachments: The superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) and retaining ligaments have greater tension and strength
- Increased subcutaneous tissue density: Fibrous subcutaneous tissue requires more aggressive dissection techniques
Vascular Considerations
The male face demonstrates a more dense vascular network, particularly in the beard-bearing areas. This increased vascularity presents several surgical implications:
- Higher intra-operative bleeding risk requiring meticulous hemostasis
- Enhanced bruising potential in the postoperative period
- Consideration for preoperative optimization of bleeding risk factors
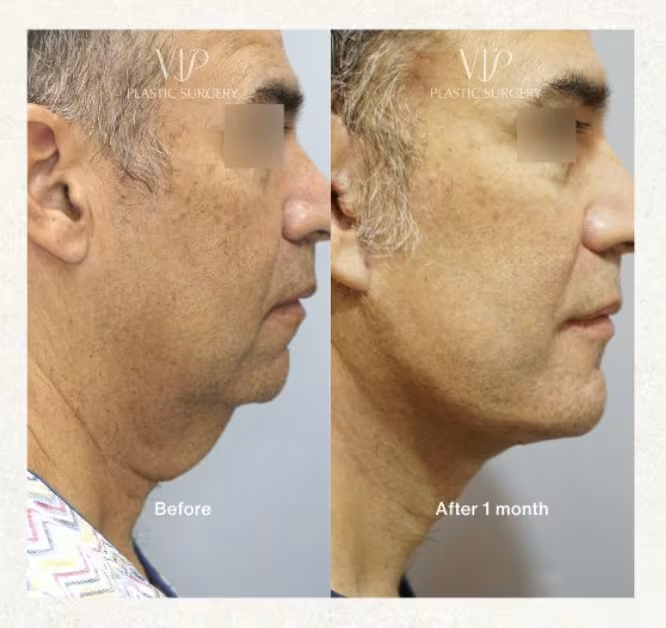
Neck Anatomy
Male patients frequently present with specific neck anatomy challenges:
- Submandibular gland hypertrophy: Enlarged salivary glands can compromise jawline definition
- Prominent platysma bands: Stronger platysma muscle requires aggressive correction
- Increased submental fat deposition: Often requires direct excision or liposuction
- Lower hyoid position: May limit the degree of achievable neck improvement
Surgical Planning Considerations
Incision Design
Incision planning in male patients requires careful consideration of hair-bearing patterns:
- Temporal region: Incisions must respect the temporal hair pattern and avoid visible scarring in areas of hair recession
- Preauricular approach: Modified to follow the natural junction of beard and non-hair-bearing skin
- Postauricular design: Adjusted based on posterior hairline configuration
- Submental access: When indicated, carefully placed within natural skin creases
SMAS Dissection Techniques
The stronger SMAS layer in male patients necessitates modified techniques:
- Extended SMAS dissection may be required for adequate mobilization
- Plication techniques must account for increased tissue resistance
- Vector of lift adjusted to maintain masculine facial contours
- Consideration for deep plane techniques in selected cases
Specialized Techniques
Deep Neck Contouring
For optimal cervical rejuvenation in male patients, deep neck surgery may be indicated:
- Partial submandibular gland reduction: Performed through a submental approach to improve jawline definition
- Digastric muscle modification: Anterior belly reduction or plication when indicated
- Subplatysmal fat excision: Direct removal of deep cervical fat deposits
- Midline platysmal plication: Extended corset platysmaplasty for durable neck contour improvement
Facial Fat Grafting
Strategic volume restoration maintains masculine facial features:
- Conservative fat grafting to address volume loss without feminization
- Focus on angular facial regions rather than convexities
- Avoidance of excessive malar augmentation
- Attention to temporal hollowing correction
Postoperative Considerations
Hemostasis and Drainage
The increased bleeding tendency in male patients requires specific postoperative management:
- Extended use of surgical drains may be necessary
- Close monitoring for hematoma formation in the first 24-48 hours
- Aggressive management of blood pressure fluctuations
- Consideration for overnight observation in selected cases
Scar Management
Scar optimization in male patients presents unique challenges:
- Hair follicle preservation during incision closure
- Modified suture techniques in beard-bearing areas
- Extended scar maturation period due to thicker dermis
- Potential for laser therapy in visible scar areas
Expected Outcomes
Well-executed male facelift surgery should achieve:
- Restoration of jawline definition with preservation of masculine angles
- Improvement in neck contour without over-correction
- Natural-appearing results that avoid an “operated” appearance
- Maintenance of normal beard growth patterns
- Preservation of masculine facial characteristics
Male facelift surgery requires a comprehensive understanding of gender-specific anatomical variations and modified surgical techniques. Successful outcomes depend on careful preoperative planning, meticulous surgical technique, and appropriate postoperative management. When these principles are properly applied, male patients can achieve significant facial rejuvenation while maintaining their masculine appearance and avoiding the challenges of surgical intervention.
Updated October 13th, 2025
VIP Plastic Surgery Clinic, Korea